Grape Root Borer on Grapes
Return to Insect Pests
Grape root borer (Vitacea polistiformis) is potentially the most destructive insect attacking grapes in Kentucky. Adults are brown moths with thin yellow bands on their abdomens; they resemble paper wasps. Front wings are brown, while hindwings are clear. Larvae are 11⁄2 inch long when mature and have a retractable brown head. The root borer life cycle takes 2 years to complete. Damage occurs when larvae tunnel into larger roots and crowns of vines. Pupal cases appear protruding from bases of vines at soil level. Aboveground symptoms include poor vine growth, reduced fruit set, and vine loss.
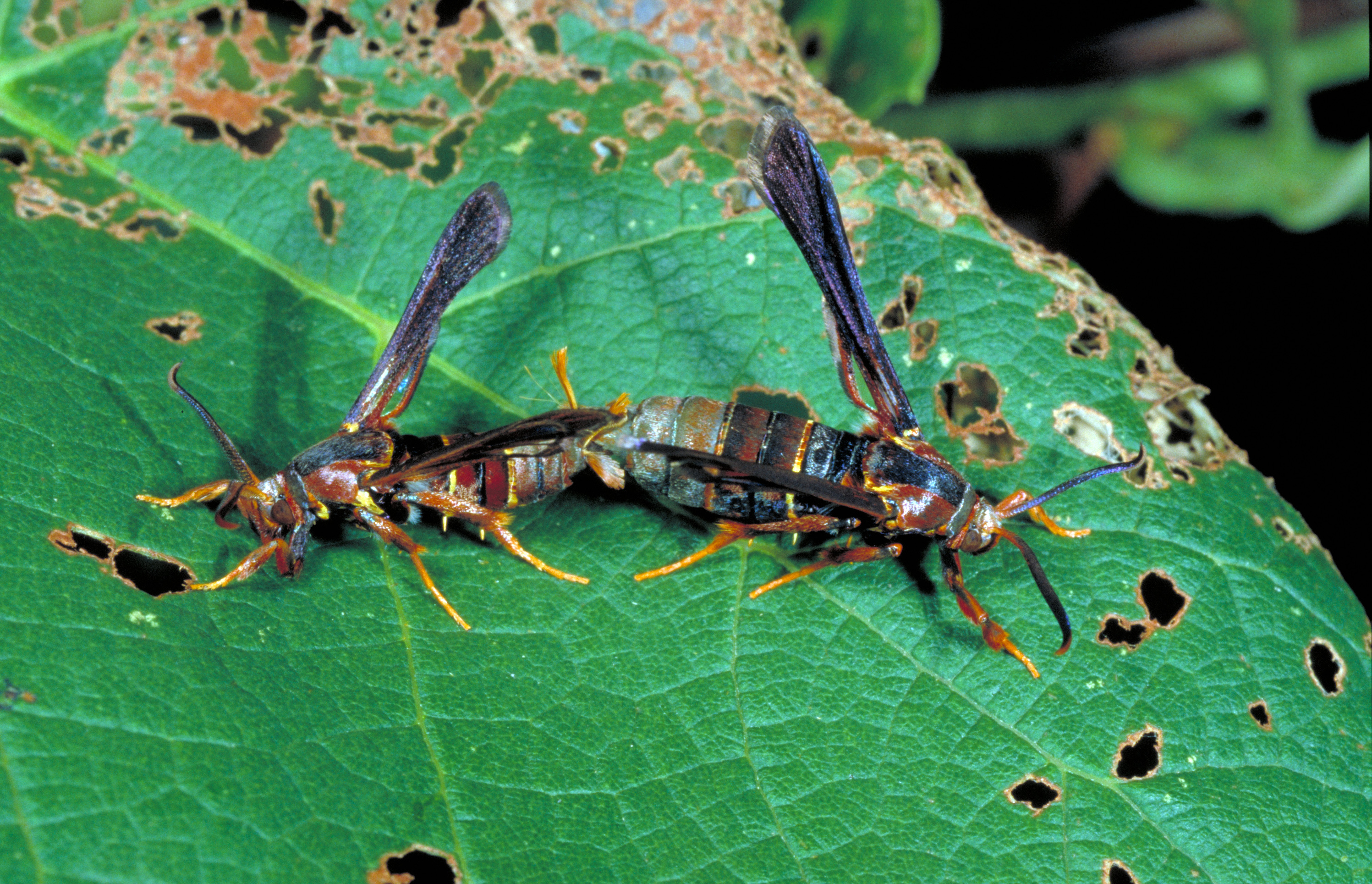

A mating pair of grape root borer moths.
(Photo: Ric Bessin, University of Kentucky)
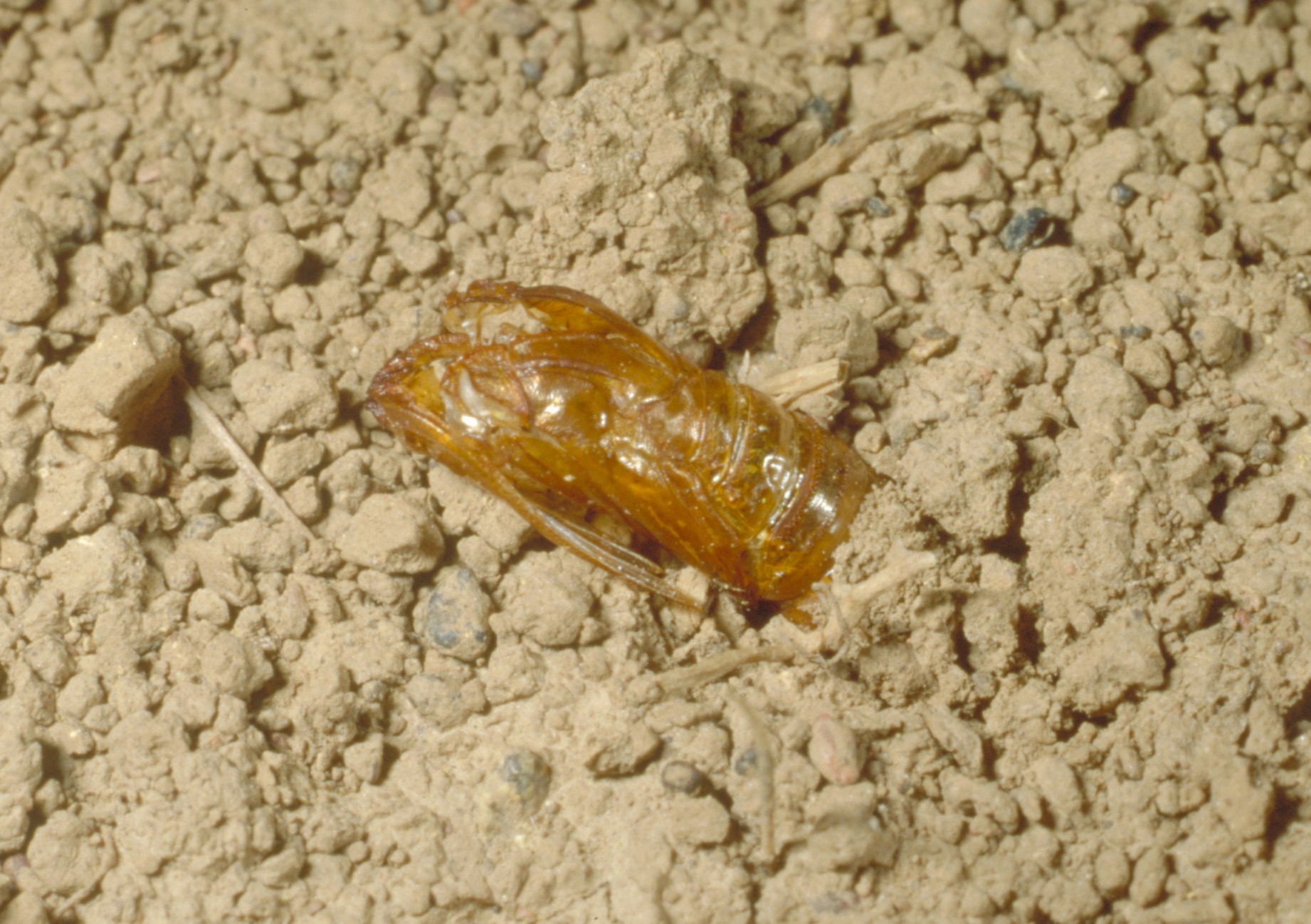

Grape root borer pupal case partially protruding from the soil.
(Photo: Ric Bessin, University of Kentucky)
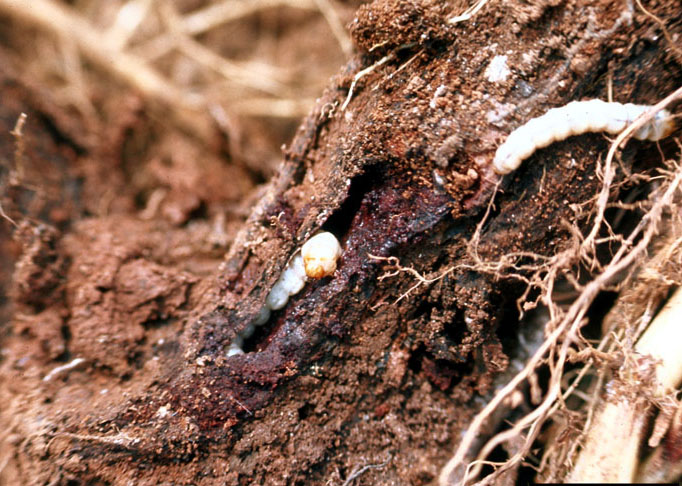
Grape root borer larvae causing root damage.
(Photo: H.C. Ellis, University of Georgia, Bugwood.org)
Management:
- Eliminate weeds around bases of vines to reduce egg-laying sites and to improve spray coverage.
- Monitor protruding pupal cases (especially in late summer).
- Apply insecticides around bases of vines.
- In small plantings and backyard settings, apply plastic mulch, which provides an effective barrier and prevents larvae from burrowing underground.
