White-Tailed Deer and Elk Damage in Peach
Return to Wildlife
White-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) and elk (Cervus canadensis) consume new growth and fruit, depending on the time of year. During spring and summer, deer and elk clip leaves and new shoots, leaving behind distinctive angled torn edges on twigs. They also consume ripe fruit, but this is generally minor relative to the damage caused by browsing (branches and buds) and antler rubbing by males during autumn.
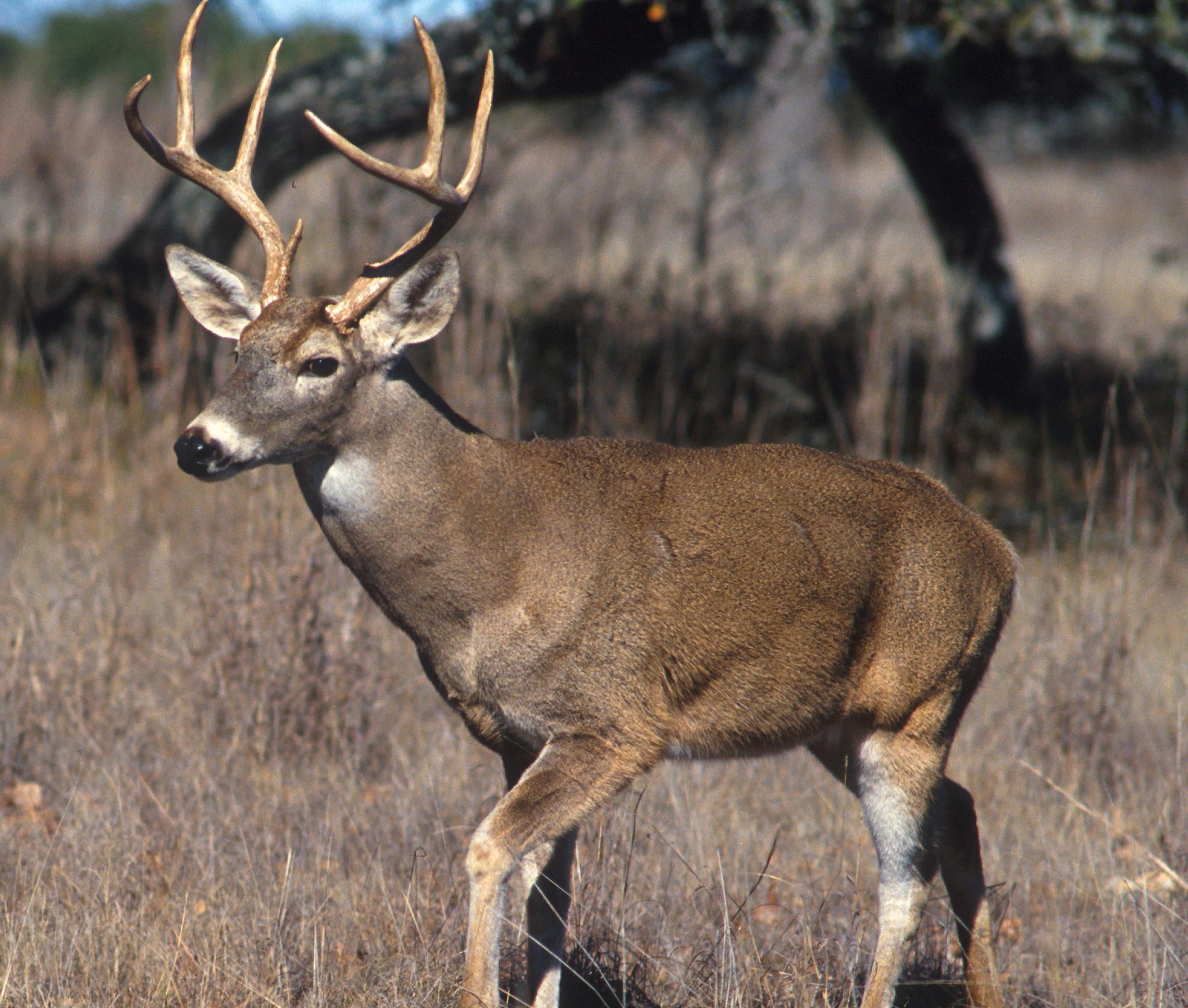

White-tailed deer.
(Photo: Scott Bauer, USDA Agricultural Research Service)
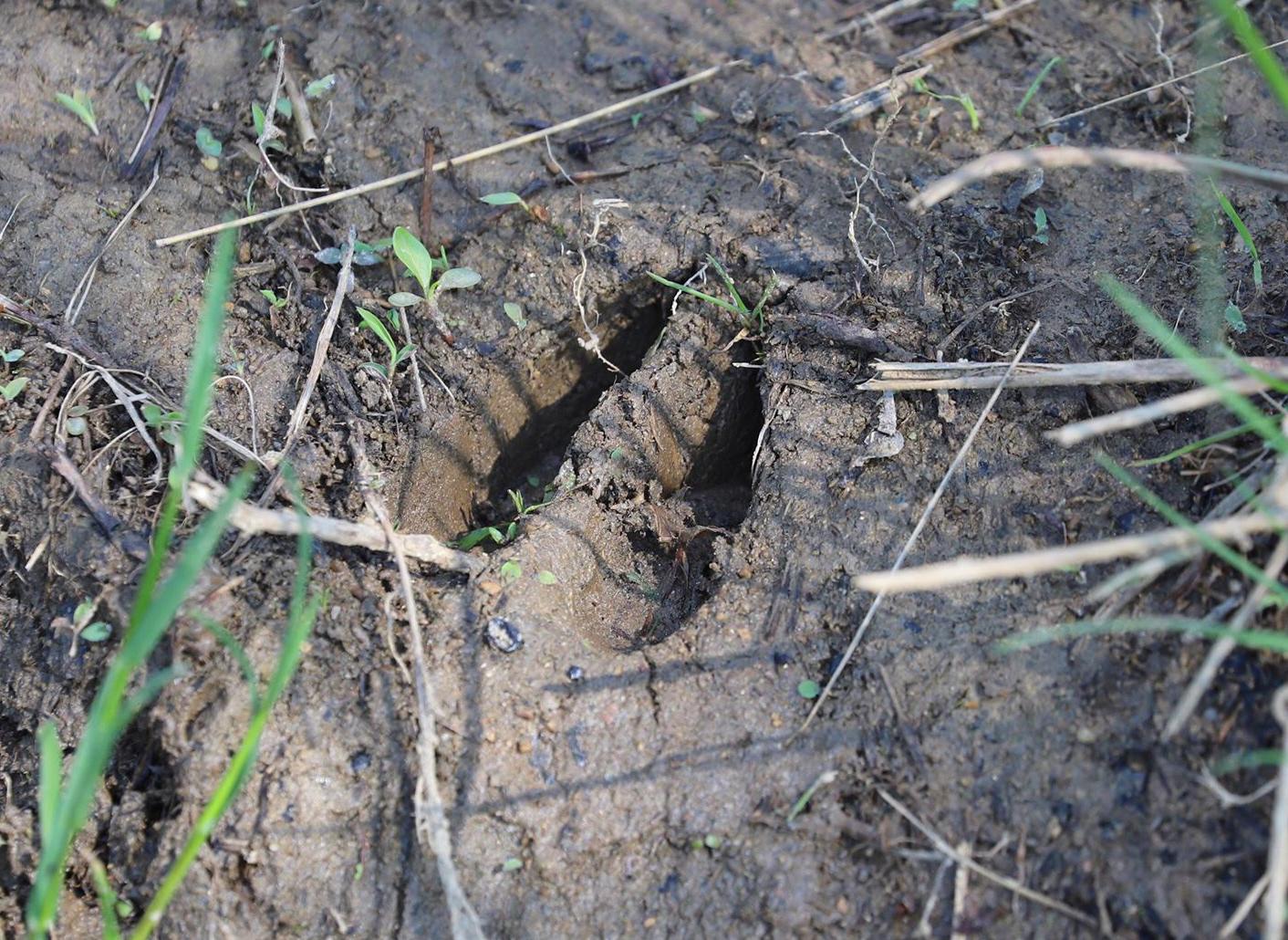

White-tailed deer track.
(Photo: Teddy Fisher)
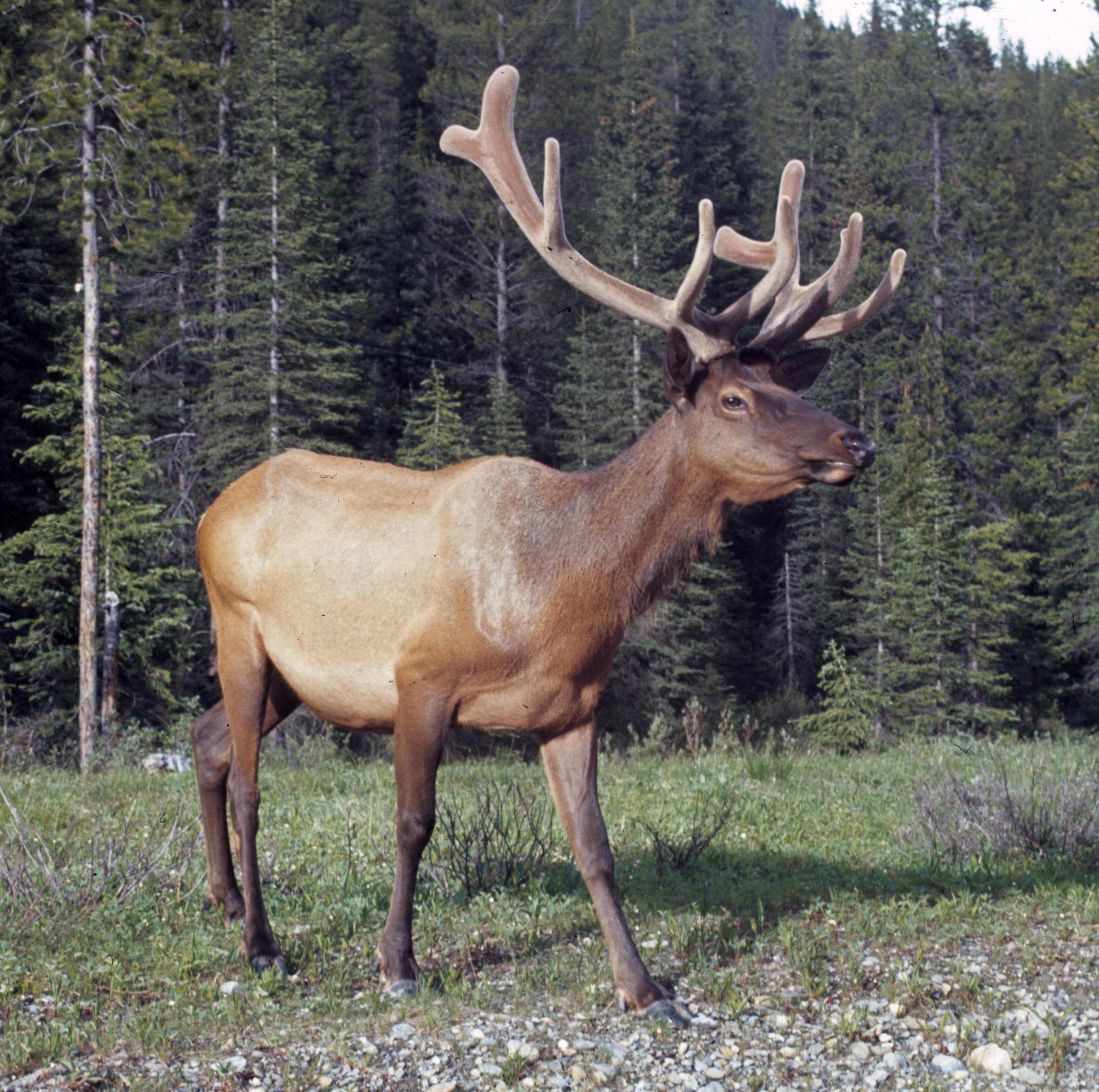

Elk.
(Photo: Alfred Viola, North Eastern University)
Elk track.
(Photo: U.S. National Parks Service)
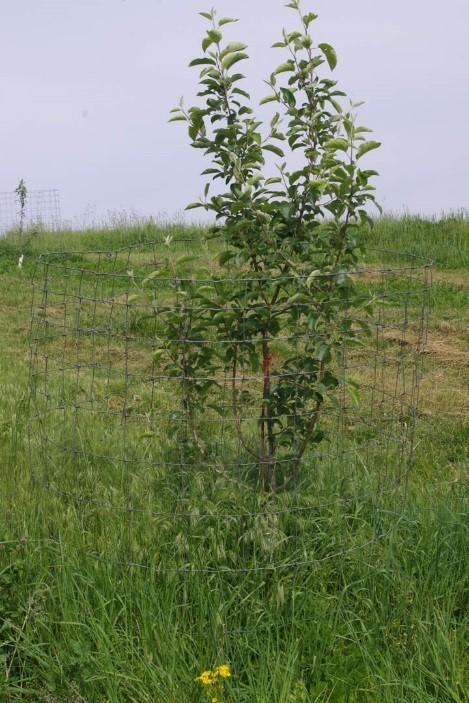

Install small fences to protect from deer rubbing and over-browsing.
(Photo: Matthew Springer, University of Kentucky)
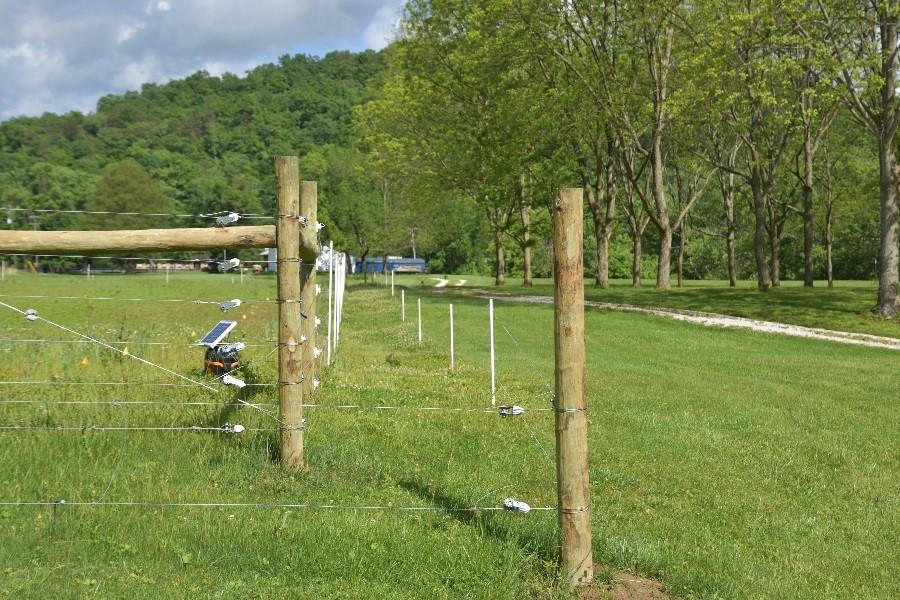

Use off-set electric fence to restrict access by deer and elk.
(Photo: Matthew Springer, University of Kentucky)
Management:
- Protect plants using 8-foot high metal fencing for deer and elk; where elk are not present, a plastic 8-foot fencing is effective against deer.
- Protect newly planted trees or saplings using small fences.
- Off-set (double wire) and overhanging slant electric fence designs are also effective in preventing access to plantings.
- Reduce the overall deer population on the property through hunting.
